Identification key to Brachymyrmex species
This key to the workers of Brachymyrmex is based on Ortiz-Sepulveda et al., 2019.
1
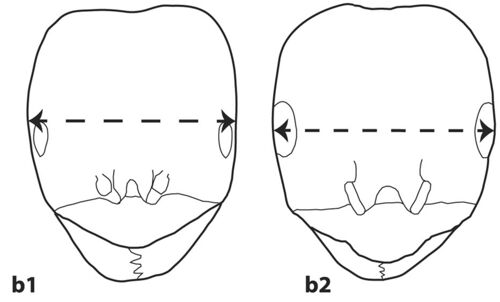
- Clypeus with a single long apical hair near the anterior margin, two lateral hairs medially and two hairs near the toruli (Fig. 5(a1)); monomorphic => 2
- Clypeus with a row of long thick hairs near the anterior margin (Fig. 5(a2)), remaining pilosity not as above; dimorphic => 39
2
return to couplet #1
- Metathoracic spiracles tumuliform (i.e., strongly protruding dorsally) (Fig. 6(a1)); known only from Brazil => 3
- Metathoracic spiracles not (Fig. 6(a2)) or slightly protruding but not tumiliform (Fig. 6(a3)); naturally occurring throughout the Neotropics => 5
3
return to couplet #2
- Toruli surpassing the posterior clypeal margin in oblique anterodorsal view (Fig. 5(a3)); head and mesosoma smooth and shiny => 4
- Toruli touching the posterior clypeal margin but never surpassing it in oblique anterodorsal view (Fig. 5(a2)); head and mesosoma finely punctate and opaque => Brachymyrmex brasiliensis
4
return to couplet #3
- Mesosoma without erect hairs; gaster with scattered long erect hairs, except for the first segment which has dense yellowish pubescence => Brachymyrmex feitosai
- Mesosoma with two erect hairs on pronotum and two on mesonotum; gaster with scattered long erect hairs, also on the first segment => Brachymyrmex delabiei
5
return to couplet #2
- Dorsum of the head, mesosoma and gaster with thick erect black hairs (as in Nylanderia) that contrast with the body color (head and gaster may be darker than mesosoma) => Brachymyrmex cavernicola
- Dorsum of the head, mesosoma and gaster without hairs, or with thin hairs that do not contrast with the body color => 6
6
return to couplet #5
- Eyes positioned below the cephalic midline (Fig. 5(b1)), with three or four ommatidia along the maximal diameter of the eye (EL) (Fig. 5(c1)) => 7
- Eyes usually positioned on the cephalic midline (Fig. 5(b2)), with more than four ommatidia along the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(c2)) => 9
7
return to couplet #6
- Mesonotum not bulging dorsally above the pronotum in lateral view (Fig. 6(b1)) => 8
- Mesonotum bulging dorsally above the pronotum in lateral view (Fig. 6(b2)) => Brachymyrmex modestus
8
return to couplet #7
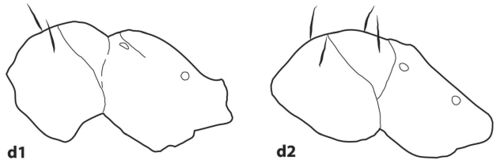
- Scapes short, just reaching the posterior margin of the head or surpassing it by a length shorter than the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d1, d2)) => Brachymyrmex donisthorpei
- Scapes long, surpassing the posterior margin of the head by a length approximately equal to the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3)) => Brachymyrmex myops
9
return to couplet #6
- Two erect hairs between the metathoracic spiracles => 10
- Without erect hairs between the metathoracic spiracles => 11
10
return to couplet #9
- Scapes surpass the posterior cephalic margin by a length of approximately 1.5× the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3): 2A ≤ B); hairs on scapes decumbent; body uniform in color (usually dark brown) => Brachymyrmex admotus
- Scapes surpass the posterior cephalic margin by a length of approximately 1.0× the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3): 2A > B); hairs on scapes appressed; head and mesosoma light brown, gaster darker => Brachymyrmex bonariensis
11
return to couplet #9
- Dorsal margin of the mesosoma having a marked sinusoidal shape (Fig. 6(c)) => 12
- Dorsal margin of the mesosoma not sinusoidal or only of sub-siusoidal shape (Figs. 6(a2, a3, b1, b2, d1, d2, e1 ,e2)) => 13
12
return to couplet #11
- Clypeus with its medial anterior portion forming a “lip” (Fig. 5(e1)); head and mesosoma partially or completely alveolate (sometimes alveolate-strigate); dorsum of the mesosoma with many erect hairs; body uniform in color => Brachymyrmex nebulosus
- Clypeus without anteromedial “lip” (Fig. 5(e2)); entire body non-alveolate; dorsum of the mesosoma without erect hairs; head and gaster black;mesosoma yellowish => Brachymyrmex bicolor
13
return to couplet #11
14
return to couplet #13
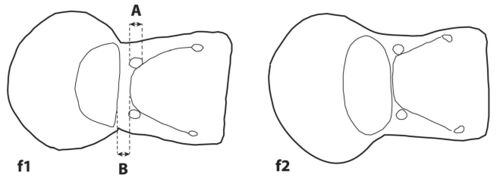
- Metanotal groove wider than the diameter of the metathoracic spiracles (Fig. 6(f1): A ≤ B); scapes surpassing the posterior margin of the head by approximately 1.0× the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3)); gaster with scattered pubescence (Fig. 6(g1)) => Brachymyrmex santschii
- Metanotal groove narrower than the diameter of the metathoracic spiracles (Fig. 6(f2): A > B); scapes just reaching the posterior margin of the head (Fig. 5(d2)); gaster with dense pubescence (Fig. 6(g2)) => Brachymyrmex iridescens
15
return to couplet #13
- Mesometanotal suture inconspicuous (Fig. 6(d1)) => 16
- Mesometanotal suture readily visible (Fig. 6(d2)) => 17
16
return to couplet #15
- Pronotum without erect hairs; scapes short or reaching the posterior margin of the head (Fig. 5(d1, d2)); gaster with dense pubescence (Fig. 6(g2)) => Brachymyrmex flavidulus
- Pronotum with two erect hairs (Fig. 6(d1)); scapes surpassing the posterior margin of the head (Fig. 5(d3)); gaster without dense pubescence, but with scattered appressed hairs (Fig. 6(g1)) => Brachymyrmex minutus
17
return to couplet #15
- Gaster with dense appressed or decumbent pubescence (Fig. 6(g2)) => 18
- Gaster with sparse pubescence, but with scattered, appressed hairs (Fig. 6(g1)) => 28
18
return to couplet #17
- Metanotal groove absent or when present shallow and narrower than the diameter of the metathoracic spiracles (Fig. 6(f2): A > B) => 19
- Metanotal groove deep and wider than the diameter of the metathoracic spiracles (Fig. 6(f1): A ≤ B) => 26
19
return to couplet #18
- Mesonotumbulging dorsally above the pronotum in lateral view (Fig. 6(b1)) => 20
- Mesonotum not bulging dorsally above the pronotum in lateral view (Fig. 6(b2)) => 22
20
return to couplet #19
- Scapes just reaching the posterior margin of the head or surpassing it by a length of less than 1.0× the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d2,d3): A > B) => 21
- Scapes surpassing the posterior margin of the head by a length of approximately 1.0× the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3): A ≈ B) => Brachymyrmex heeri
21
return to couplet #20
- Body usually dark brown; eye with on average nine ommatidia along its maximal diameter; scapes on average > 0.5 mm; known only from South America => Brachymyrmex giardi
- Body yellowish; eye with on average six ommatidia along its maximal diameter; scapes on average < 0.5 mm; known only from Canada,Mexico, USA => Brachymyrmex depilis
22
return to couplet #19
23
return to couplet #22
- Scapes not or barely reaching the posterior margin of the head (Fig. 5(d1, d2)) => Brachymyrmex fiebrigi
- Scapes surpassing the posterior margin of the head (Fig. 5(d3)) => 24
24
return to couplet #23
- About six erect hairs on the pronotum and two on the mesonotum, each hair with a length of about 2.0× the maximal diameter of the eye; known only from the Bahamas => Brachymyrmex bahamensis
- Two erect hairs on the pronotum and two on the mesonotum, each with a length shorter than the maximal diameter of the eye; widespread => Brachymyrmex termitophilus
25
return to couplet #22
- Dorsum of the head and mesosoma with light-colored, dense pubescence; gaster with dense appressed pubescence; eye with on average 11 ommatidia along its maximal diameter, head on average long (HL1 > 0.5 mm) and wide (HW> 0.4 mm) => Brachymyrmex cordemoyi
- Dorsum of the head and mesosoma with less conspicuous dense pubescence; gaster with dense decumbent pubescence; eye with on average nine ommatidia along its maximal diameter, head on average short (HL1 < 0.5 mm) and narrow (HW < 0.4 mm) => Brachymyrmex obscurior
26
return to couplet #18
- Dorsum of the mesosoma without conspicuous sculpture; metathoracic spiracles fully dorsal in position; dorsal margin of the mesonotum strongly antero-posteriorly inclined (Fig. 6(e1)) => Brachymyrmex sosai
- Dorsum of the mesosoma with imbricate sculpture; metathoracic spiracles in dorsolateral position; dorsal margin of the mesonotum not or slightly antero-posteriorly inclined (Fig. 6(e2)) => 27
27
return to couplet #26
- Second segment of the antennal funiculus shorter than the first antennal segment (Fig. 5(g1): S2 < S1); scapes with appressed hairs; metathoracic spiracles protruding slightly dorsally, but not tumiliform (Fig. 6(a3)); hairs lighter in color than the body, which is brownish => Brachymyrmex attenuatus
- Second segment of the antennal funiculus as long or longer than the first antennal segment (Fig. 6(g2): S2 ≥ S1); scapes with decumbent hairs; methatoracic spiracles not protruding (Fig. 6(a2)) hairs darker in color than the body, which is yellowish => Brachymyrmex antennatus
28
return to couplet #17
- Eyes large, with a maximal diameter > 1/4th of the length of the head (HL1), usually with >14 ommatidia along their maximal diameter => Brachymyrmex oculatus
- Eyes small, with a maximal diameter of approximately 1/4th the length of HL1, typically with <14 ommatidia along their maximal diameter => 29
29
return to couplet #28
- Metanotal groove absent, or, when present, shallow and narrower than the diameter of the metathoracic spiracles (Fig. 6(f2): A > B) => 30
- Metanotal groove deep and wider than the diameter of the metathoracic spiracles (Fig. 6(f1): A ≤ B.) => 34
30
return to couplet #29
- Head and thorax yellowish; gaster black or yellowish with a black spot, OI2 usually > 27 => Brachymyrmex pictus
- Body of uniform color, OI2 usually < 25 => 31
31
return to couplet #30
- Body yellowish, usually with a narrow mesonotum (MW ~ 16) and 8–9 ommatids along the maximum diameter of the eye => 32
- Body brownish or dark brown, usually with a wide mesonotum (MW ~ 20 or more) and 10 or more ommatids along the maximum diameter of the eye => 33
32
return to couplet #31
- Scapes surpassing the posterior margin of the head by a length exceeding the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3): A < B) => Brachymyrmex aphidicola
- Scapes surpassing the posterior margin of the head by a length smaller than or equal to the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3): A ≥ B) => Brachymyrmex australis
33
return to couplet #31
- Scapes surpassing the posterior margin of the head by a length smaller than the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3): A > B); usually with two erect hairs on the pronotum and two on the mesonotum => Brachymyrmex patagonicus
- Scapes surpassing the posterior margin of the head by a length approximately equal to the maximal diameter of the eye (Fig. 5(d3): A ≈ B); usually with more than two erect or decumbent hairs on the pronotum and two erect hairs on the mesonotum => Brachymyrmex bruchi
34
return to couplet #29
- Legs and antennae with erect hairs; second segment of the antennal funiculus as long as or longer than the first (Fig. 5(g2): S2 ≥ S1) => Brachymyrmex gaucho
- Legs and antennae with decumbent or appressed hairs; second segment of the antennal funiculus shorter than the first(Fig. 5(g1): S2 < S1) => 35
35
return to couplet #34
- Mesonotum not bulging dorsally above the pronotum in lateral view (Fig. 6(b2)); metathoracic spiracles low, not protruding dorsally (Fig. 6(a2)) => Brachymyrmex musculus
- Mesonotum bulging dorsally above the pronotum in lateral view (Fig. 6(b1)); metathoracic spiracles protruding slightly in lateral view but not tumiliform in shape (Fig. 6(a3)) => 36
36
return to couplet #35
- Head and thorax yellow or brown, gaster darker => Brachymyrmex coactus
- Body uniform in color => 37
37
return to couplet #36
- Head with dense decumbent pubescence (Fig. 5(f1)) => Brachymyrmex tristis
- Head with sparse decumbent pubescence (Fig. 5(f2)) => 38
38
return to couplet #37
- Mesonotum laterally extended and therefore oval in dorsal view (Fig. 6(h1)); body light brown => Brachymyrmex degener
- Mesonotum almost circular in dorsal view (Fig. 6(h2)); body dark brown or black => Brachymyrmex gagates
39
return to couplet #1
- Mesosoma mostly smooth and shiny, except for longitudinal striations restricted to the metapleura; body uniform light brown => Brachymyrmex micromegas
- Mesosoma entirely covered with fine longitudinal striations; gaster darker than the rest of the body => Brachymyrmex pilipes